library(tidyverse)
dist <-
tibble(
# Gridwerte bestimmen:
p_grid = seq(from = 0, to = 1, length.out = 20),
# Priori-Wskt bestimmen:
prior = rep(1, times = 20)) %>%
mutate(
# Likelihood berechnen:
likelihood_1 = dbinom(3, size = 3, prob = p_grid), # WWW
likelihood_2 = dbinom(3, size = 4, prob = p_grid), # WWWL
likelihood_3 = dbinom(5, size = 7, prob = p_grid), # LWWLWWW
# unstand. Posterior-Wskt:
unstand_post_1 = likelihood_1 * prior,
unstand_post_2 = likelihood_2 * prior,
unstand_post_3 = likelihood_3 * prior,
# stand. Post-Wskt:
std_post_1 = unstand_post_1 / sum(unstand_post_1),
std_post_2 = unstand_post_2 / sum(unstand_post_2),
std_post_3 = unstand_post_3 / sum(unstand_post_3)
) Rethink2m1
probability
bayesbox
rethink-chap2
string
Aufgabe
This question is taken from McElreath, R. (2020). Statistical rethinking: A Bayesian course with examples in R and Stan (2. Ed.). Taylor and Francis, CRC Press.
2M1. Recall the globe tossing model from the chapter (also see exercise globus1).
Compute and plot the grid approximate posterior distribution for each of the following sets of observations. In each case, assume a uniform prior for p.
- WWW
- WWWL
- LWWLWWW
Lösung
The solution is taken from this source.
Hier ist die Bayes-Box:
knitr::kable(round(dist, 2))| p_grid | prior | likelihood_1 | likelihood_2 | likelihood_3 | unstand_post_1 | unstand_post_2 | unstand_post_3 | std_post_1 | std_post_2 | std_post_3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.05 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.11 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.16 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.21 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 0.26 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 0.32 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 0.37 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 0.42 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| 0.47 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 0.53 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| 0.58 | 1 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 0.63 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| 0.68 | 1 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| 0.74 | 1 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| 0.79 | 1 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| 0.84 | 1 | 0.60 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.60 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| 0.89 | 1 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.06 |
| 0.95 | 1 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| 1.00 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Jetzt können wir das jeweilige Diagramm zeichnen:
library(ggpubr)
ggline(dist,
x = "p_grid",
y = "std_post_1")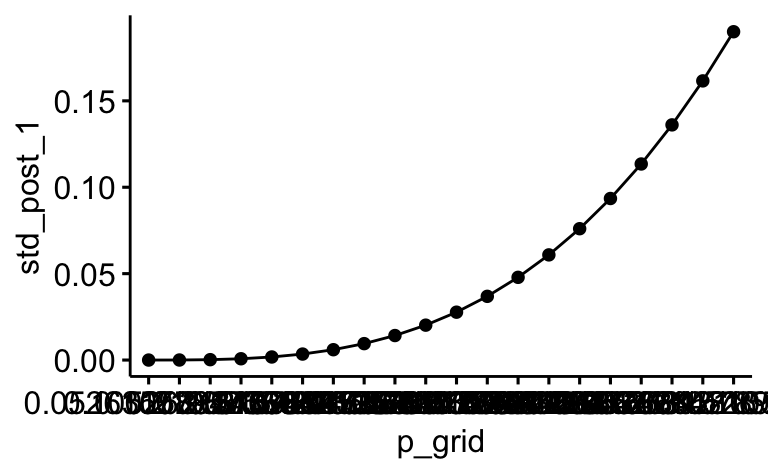
Oder mit ggplot2:
ggplot(dist) +
aes(x = p_grid, y= std_post_1) +
geom_line()+
geom_point() +
labs(x = "p(W)",
y = "Posteriori-Wahrscheinlichkeit",
title = "Daten: WWW")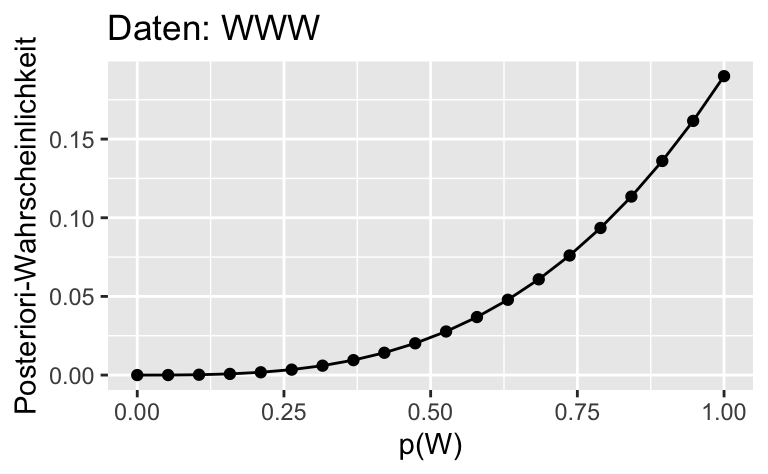
ggplot(dist) +
aes(x = p_grid, y= std_post_2) +
geom_line()+
geom_point() +
labs(x = "p(W)",
y = "Posteriori-Wahrscheinlichkeit",
title = "Daten: WWWL")
ggplot(dist) +
aes(x = p_grid, y= std_post_3) +
geom_line()+
geom_point() +
labs(x = "p(W)",
y = "Posteriori-Wahrscheinlichkeit",
title = "Daten: LWWLWWW")
Categories:
- probability
- bayesbox
- rethink-chap2
- string